When something develops as quickly as green energy, it is difficult to keep up with the latest jargon. It's easy to get lost in all the terminology. Reason for us to help you out by listing 25 green energy terms and their meanings.
Green energy terms
Our mission is to inspire and educate as many people as possible about the possibilities in saving our planet. A big part of that is explaining the basics and why we do it. You will come across the following green energy terms on a regular basis. We'd love to explain what they mean.
Climate change terms
Climate change means a significant change in temperature and weather conditions that deviates from the norm. It is one of the greatest crises facing humanity. It includes more than just global warming; it also refers to all the changes that are happening on our planet. Terms you may come across are:
CO2 footprint
This term describes the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere as a result of the behaviour of individuals, organisations or communities.
Global Warming
This English term indicates that the overall temperature of the earth's atmosphere is rising. It is thought to be caused by the greenhouse effect, which in turn is caused by increasing amounts of carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons and other pollutants in the atmosphere.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Chlorofluorocarbons are a group of chemicals consisting of chlorine, fluorine, carbon and hydrogen. In 1970, it was discovered that these substances caused a chemical reaction that is destroying the ozone layer and strongly contributing to global warming. They were found in refrigerators and spray bottles and were widely used until the early 2000s. Since then, these substances have been banned.
Ozone layer
The ozone layer is part of the Earth's atmosphere and forms a barrier over the planet. It helps to block harmful radiation from the sun.
Greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect refers to the heat of the sun that is trapped in the atmosphere. This occurs when the sun's rays reach the atmosphere but cannot be reflected back. The rays are absorbed by the greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases are all gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect by absorbing the sun's rays. The best known greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons.
Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels are formed from the remains of dead organisms over millions of years. They are non-renewable and finite. This means that they cannot be replaced when they run out.
Renewable energy terms
Renewable energy includes all renewable energy that comes from natural sources, such as wind, sun, water and geothermal heat. It includes biomass, hydroelectricity, solar energy and heat, geothermal energy and wind energy.
Biomass
Biomass is a broad umbrella term for all organic substances, such as agricultural crops, organic waste, manure and wood or woodchips.
Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy, also known as geothermal heat, is energy gained by using the heat from steam or hot water reservoirs to drive an electric generator.
Hydropower
Hydropower refers to the electricity generated by flowing water.
Solar energy
Solar energy is energy that is generated by the rays of the sun. Solar panels are often used for this purpose.
Tidal energy
Tidal power makes use of the differences between low and high tide. The energy of the moving water is used in a turbine to generate electricity.
Wave energy
Wave energy makes use of the rapidly changing water heights at sea, the waves. It is therefore very similar to tidal energy.
Wind energy
Wind energy makes use of the power of the wind. The wind currents set the blades of a wind turbine in motion and thus create electricity.
Smart Meter
A smart meter keeps track of electricity consumption in your home and shows how much electricity you are using at the moment and how much it costs. It also allows you to check your energy consumption remotely.
Low CO2 emissions
Low carbon means that you emit less carbon dioxide into the atmosphere with a particular technology.
Solar energy storage
A solar storage system ensures that the electricity you generate with your solar panels but do not use is not automatically fed back into the grid, but is instead stored.
Watt (W)
Watts is a unit of power and indicates how much energy is consumed. For example, your television may consume 80 to 400 watts per hour and a light bulb around 60 watts.
Kilowatt hour (kWh)
Kilowatt hour means one thousand watts per hour. It shows how much electricity is being consumed.
Electric car or Electric Vehicle (EV)
An electric car runs purely on electricity and uses an electric motor to propel itself. These cars emit fewer greenhouse gases than petrol or diesel cars and do not use finite energy sources.
Photovoltaic (PV)
Photovoltaic refers to the way sunlight is converted into energy.
Hybrid car
A hybrid car is a combination of an electric car and a petrol/diesel car in one. It is a more environmentally friendly alternative to petrol and diesel cars, as they emit less greenhouse gas.
Battery Electric Car or Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
A battery electric car is a car that runs only on a battery. They use no fuel or diesel and are 100 per cent electric.
Plug-in hybrid or Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
A plug-in hybrid car is a car that uses the combination of an electric battery and a petrol or diesel engine. The difference between a plug-in hybrid car and a hybrid car is that the battery of a plug-in hybrid car can be charged. A hybrid car cannot be charged via an external charger and only charges while driving. A plug-in hybrid car often has a longer range than conventional hybrid cars.
Myenergi energy terms
Our mission at myenergi is to create and innovate green energy products that help reduce your CO2 emissions and energy bills.
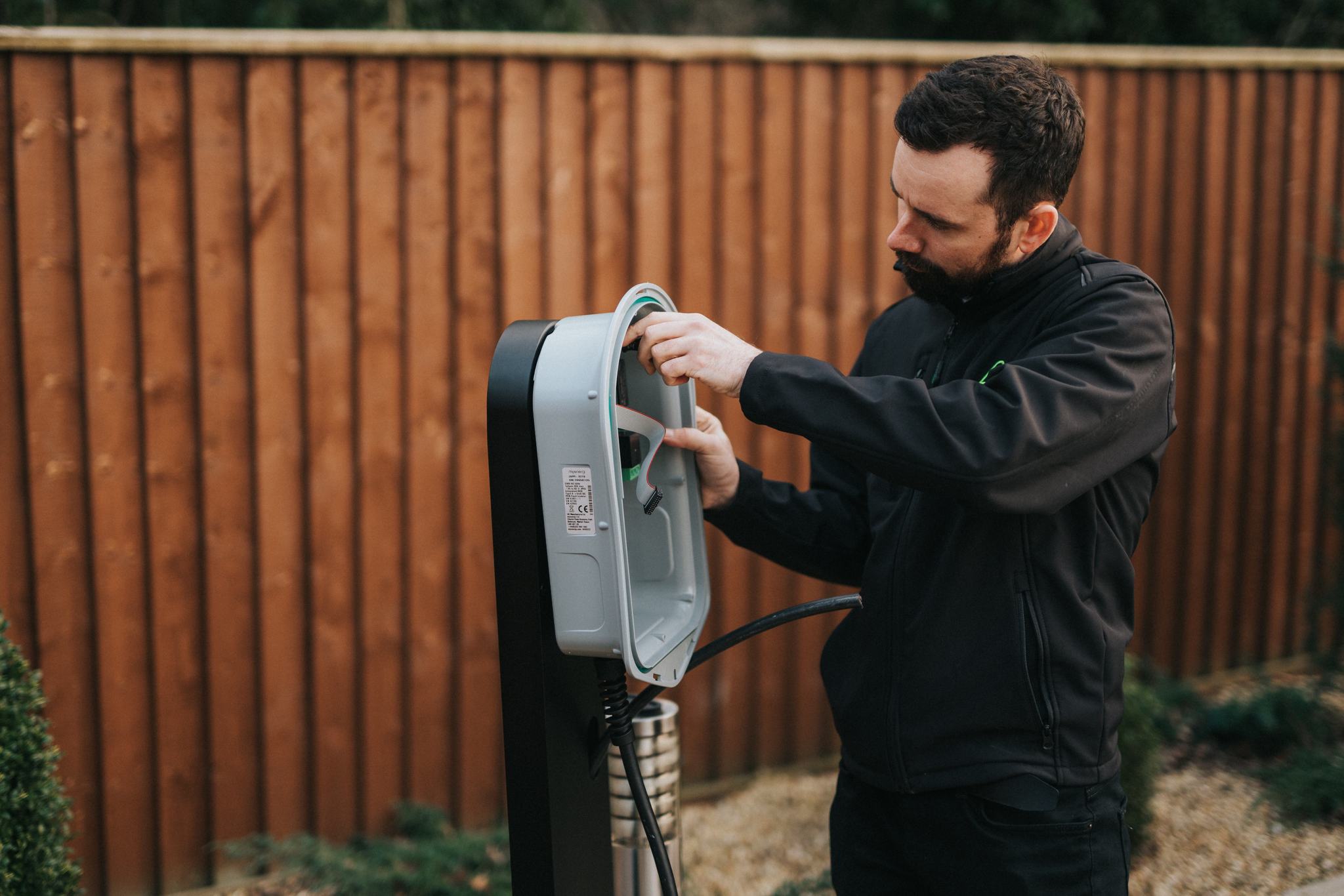
 zappi
zappi
Our smart EV charger zappi uses energy that you generate with solar panels or your own wind turbine to charge your electric car. It can also be used with energy from the grid at the most favourable rates.
eddi
eddi is an eco-smart energy converter that uses the surplus of your self-generated energy to heat your home and water.
harvi
harvi is a self-powered wireless sensor that can be used alongside zappi and eddi. The smart device can measure how much energy you consume and suggest cheaper, cleaner ways to power your car and home.
Learn more about renewable energy
At myenergi, we continue to develop new products that make the world a greener place. Together, we are working towards a green future. Want to know more about our mission? Get in touch with our green team.

 EV charging
EV charging Manage your energy
Manage your energy Maximize your energy
Maximize your energy Monitor your energy
Monitor your energy Find an installer
Find an installer Business charging station
Business charging station Pair zappi with a management platform
Pair zappi with a management platform





